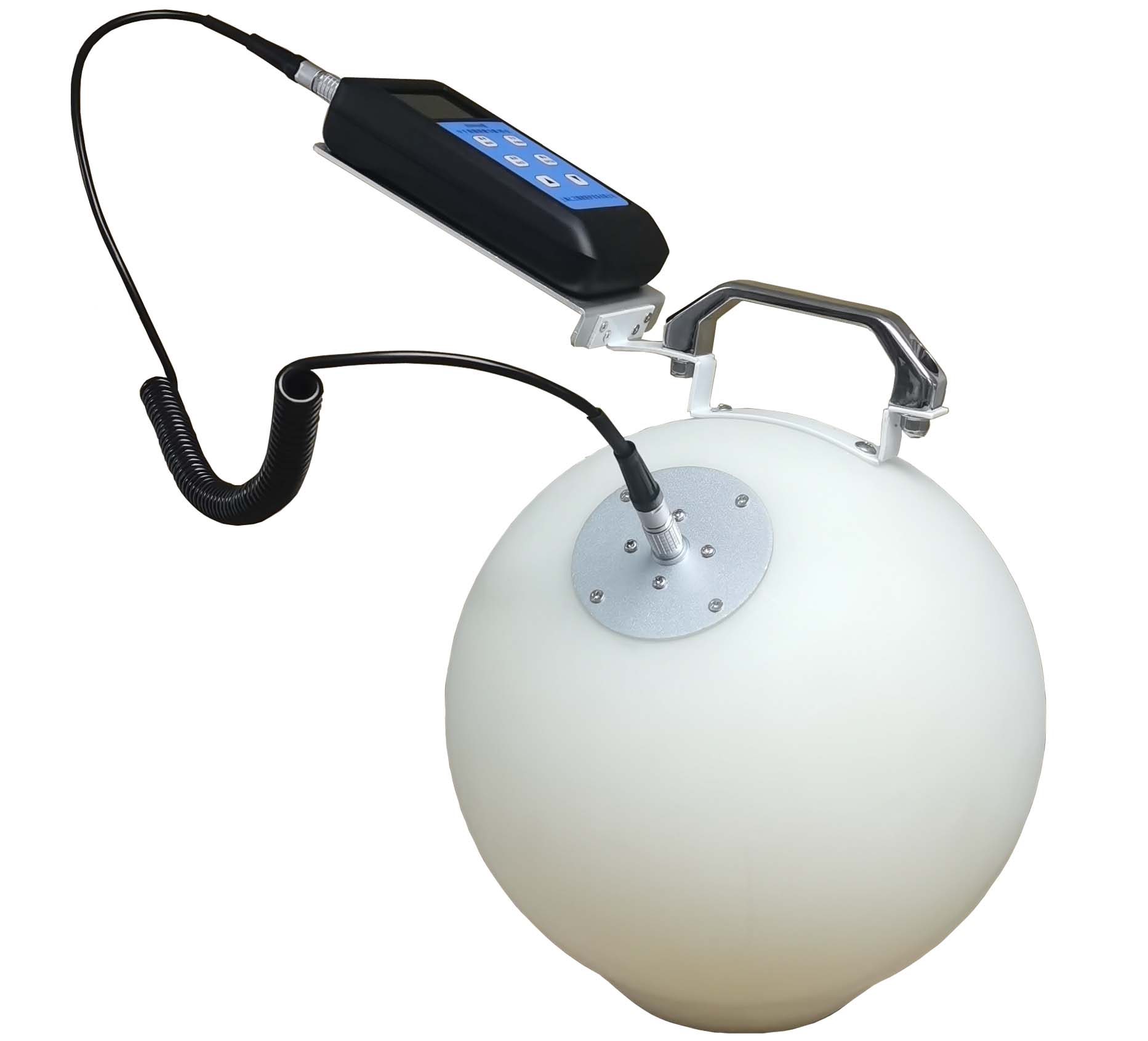


 REN800A型中子、X、γ辐射周围剂量当量(率)仪内置一个进口He-3管和一个GM管作为探测器,能同时检测中子和X、γ射线。该仪器使用方便;灵敏度高、抗γ性能好、能量响应特性好。此外通过配套的RenRiRate辐射剂量管理软件可将存储的数据读出后分析。该仪器适用于环保、化工、石油、医疗、进出口商检
REN800A型中子、X、γ辐射周围剂量当量(率)仪内置一个进口He-3管和一个GM管作为探测器,能同时检测中子和X、γ射线。该仪器使用方便;灵敏度高、抗γ性能好、能量响应特性好。此外通过配套的RenRiRate辐射剂量管理软件可将存储的数据读出后分析。该仪器适用于环保、化工、石油、医疗、进出口商检
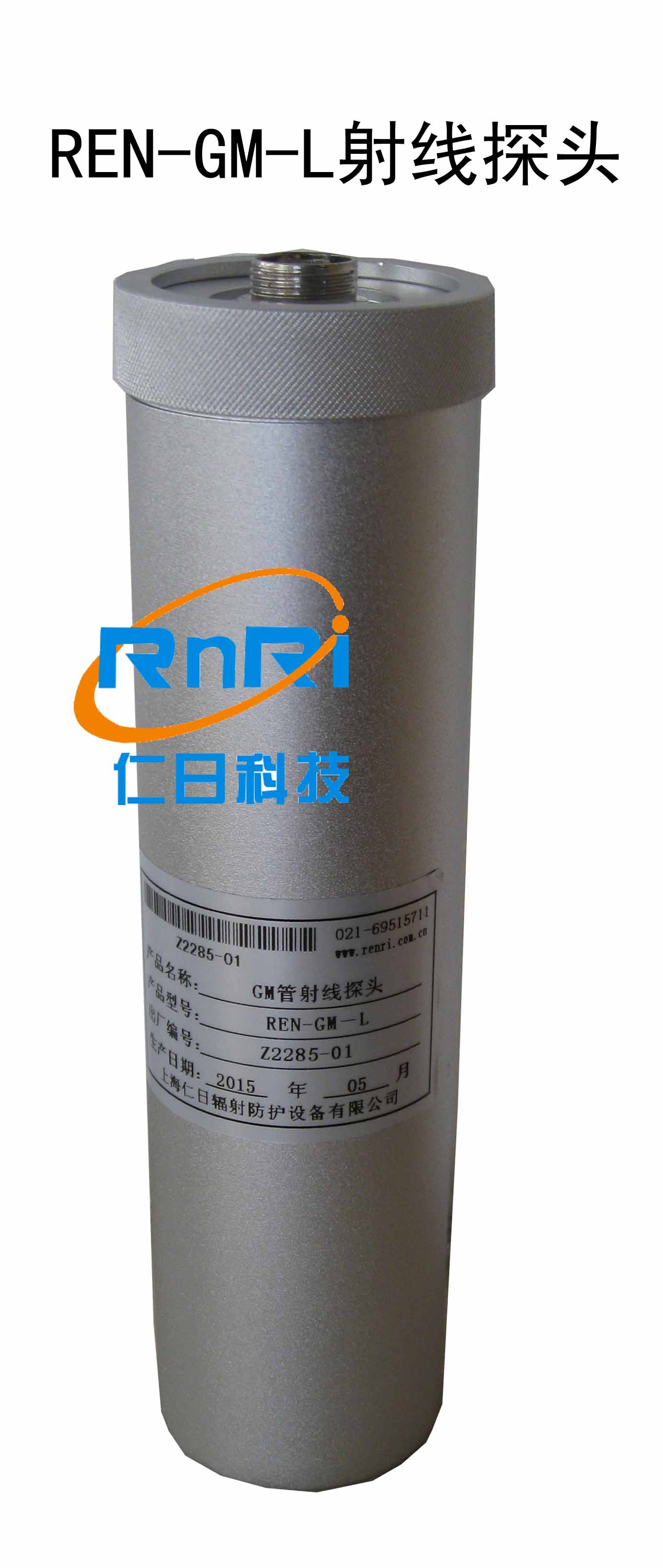 REN系列智能化辐射探头均可和REN300、REN300A、REN300B系列主机配套使用,也可以单独配套RenRiArea辐射区域监测软件使用。且具有RS485/RS232的通讯能力。所有探头均可单独外接报警灯,在超阈值的情况下就地给出声光报警。
1、测量射线类型:X、γ射线2、探测器:GM管探
REN系列智能化辐射探头均可和REN300、REN300A、REN300B系列主机配套使用,也可以单独配套RenRiArea辐射区域监测软件使用。且具有RS485/RS232的通讯能力。所有探头均可单独外接报警灯,在超阈值的情况下就地给出声光报警。
1、测量射线类型:X、γ射线2、探测器:GM管探
 单联移动式防护屏风
1、规格尺寸: H×W:1800×900 (mm)2、商品描述: 上部铅有机玻璃的高度为 H×W:240×240 (mm)3、铅当量: 铅玻璃0.5mmPb, 下部分铅当量为0.5mmpb4、外饰材料:碳素钢板喷
单联移动式防护屏风
1、规格尺寸: H×W:1800×900 (mm)2、商品描述: 上部铅有机玻璃的高度为 H×W:240×240 (mm)3、铅当量: 铅玻璃0.5mmPb, 下部分铅当量为0.5mmpb4、外饰材料:碳素钢板喷
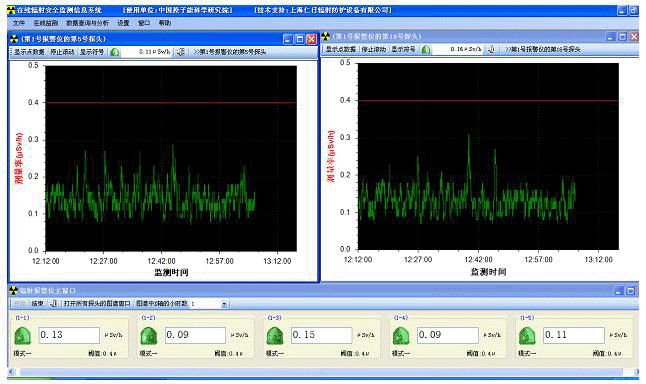 为了加强对放射源和射线装置安全运行的监督管理,保障人体健康、保护环境,根据辐射防护三原则与国家相关标准的要求,考虑人为操作失误、射线装置和放射源意外故障等原因可能引发的放射性危害,有必要建设一套在线xγ射线监测报警系统。
在线式xγ射线监测报警系统通过计算机远程集中监测,完成对放射性
为了加强对放射源和射线装置安全运行的监督管理,保障人体健康、保护环境,根据辐射防护三原则与国家相关标准的要求,考虑人为操作失误、射线装置和放射源意外故障等原因可能引发的放射性危害,有必要建设一套在线xγ射线监测报警系统。
在线式xγ射线监测报警系统通过计算机远程集中监测,完成对放射性
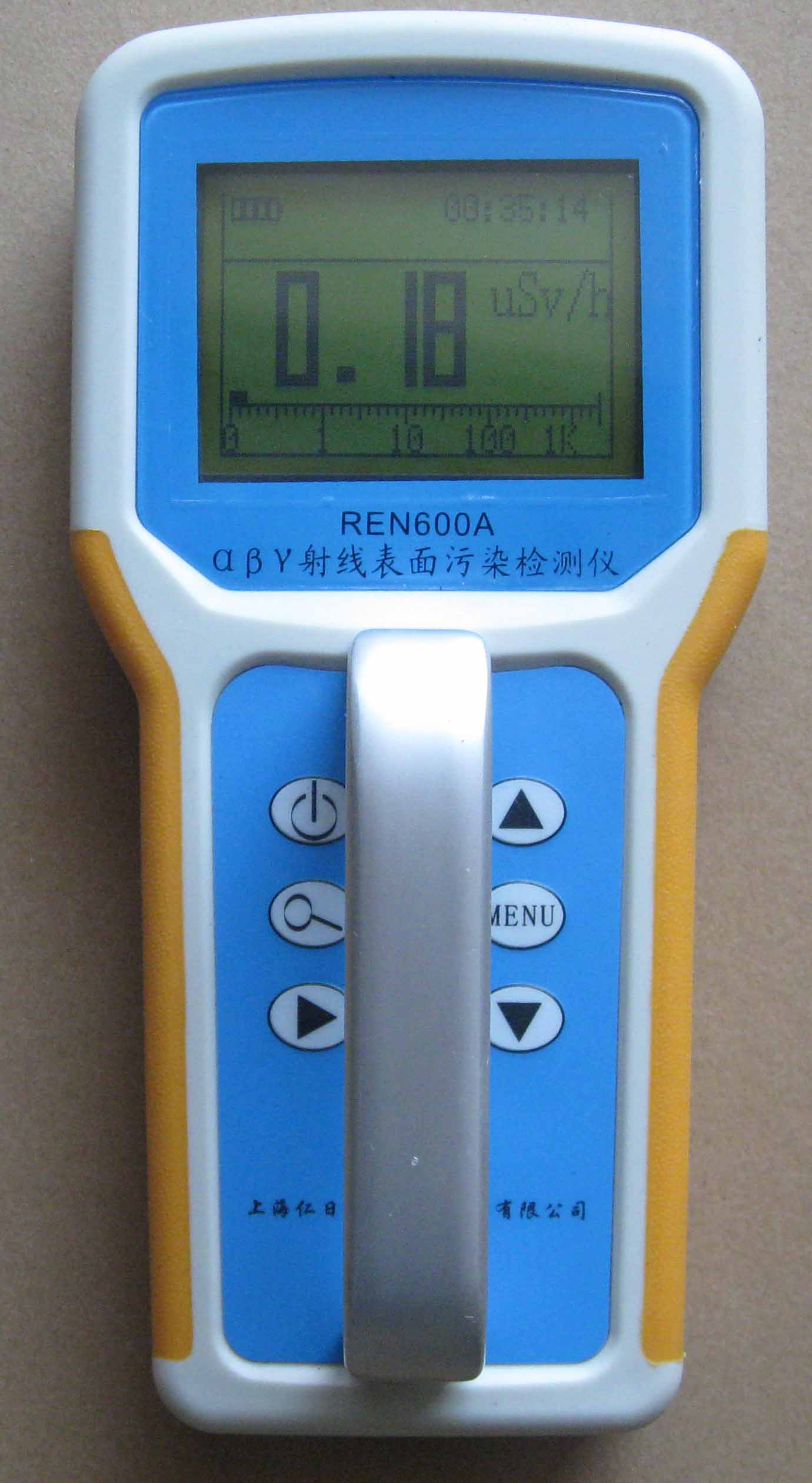 REN600A型α、β、γ射线表面污染检测仪即可检测α、β、γ射线,也能检测到X射线,它采用高速嵌入式微处器作为数据处理单元,点阵式大屏幕LCD液晶显示,读数清晰、操作方便,具有400条超大容量数据存储。仪器采用进口的大面积MICA盖革探测器,具有较高探测效率,可进行α、β辐射表面污染检测和X、γ辐
REN600A型α、β、γ射线表面污染检测仪即可检测α、β、γ射线,也能检测到X射线,它采用高速嵌入式微处器作为数据处理单元,点阵式大屏幕LCD液晶显示,读数清晰、操作方便,具有400条超大容量数据存储。仪器采用进口的大面积MICA盖革探测器,具有较高探测效率,可进行α、β辐射表面污染检测和X、γ辐
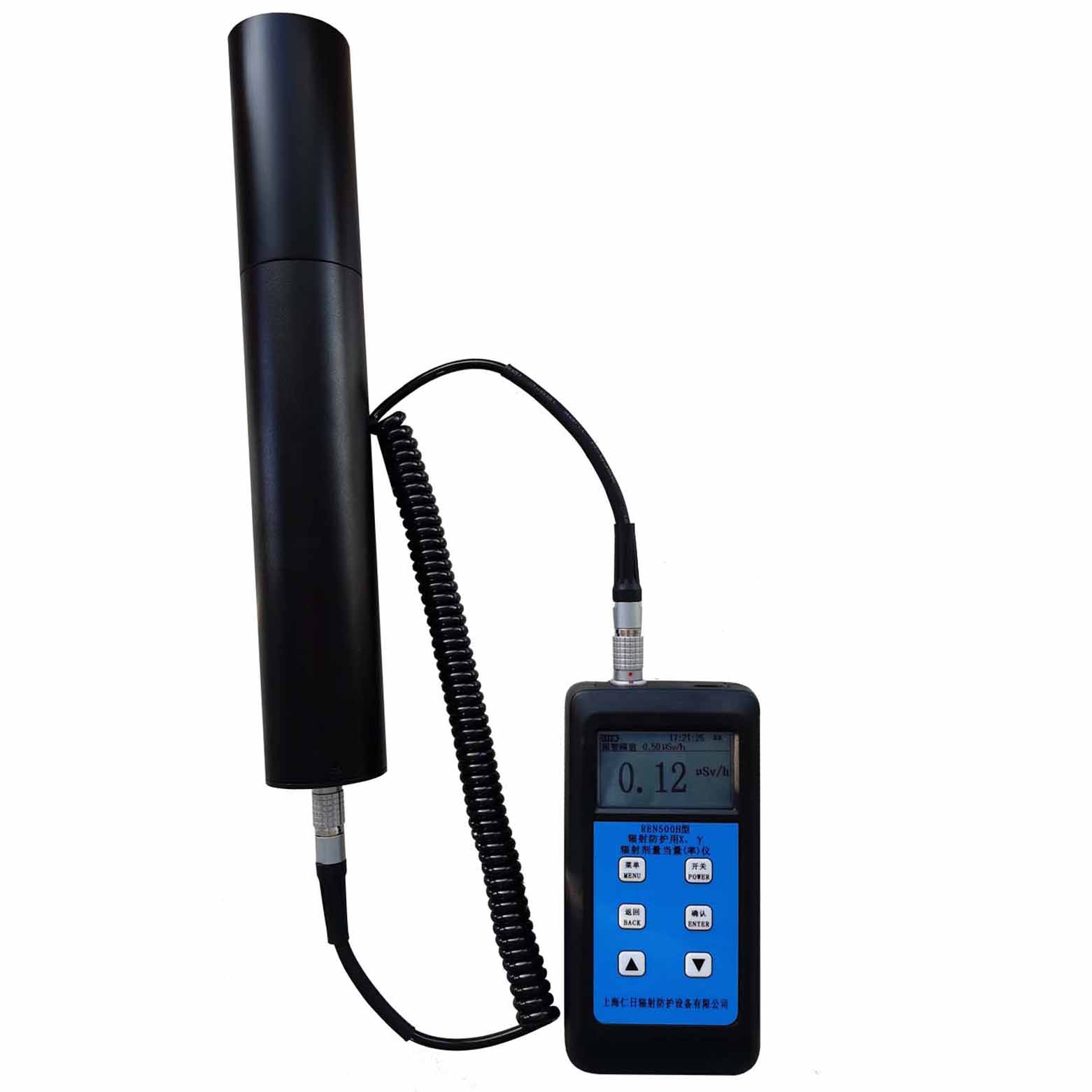 REN500H辐射防护用X、γ辐射剂量当量(率)仪是监测各种高剂量放射性工作场所的辐射剂量率专用仪器。仪器满足《环境地表γ辐射剂量率测定规范》中高剂量部分的要求。该仪器除能测高能γ射线外,还能对低能X射线进行准确的测量,具有良好的能量响应特性。此外通过配套的RenRiRate辐射剂量管理软件可将存储
REN500H辐射防护用X、γ辐射剂量当量(率)仪是监测各种高剂量放射性工作场所的辐射剂量率专用仪器。仪器满足《环境地表γ辐射剂量率测定规范》中高剂量部分的要求。该仪器除能测高能γ射线外,还能对低能X射线进行准确的测量,具有良好的能量响应特性。此外通过配套的RenRiRate辐射剂量管理软件可将存储
2006/9/9 10:05:00
氡从何处来?
室内氡的来源是多途径的,但主要是:
1、岩石(土壤)是室内氡积累的普遍而直接的来源,而且是主要的来源(当居室中各类建材的放射性符合国家标准时)。
2、构造带。构造带不是直接的氡来源,但它是地下氡汇集和迁移的通道,有时比岩石因素更重要。例如某地房屋建在裂隙不很发育的花岗岩上,在相同的其他建材条件下,室内的氡往往要比房屋建在放射性较低,而裂隙发育又相当厉害的砂岩上为低。
3、水源有时也是室内氡的重要来源,直接来自地下的、铀矿区或油气田区的水往往有较高的氡浓度。
4、在房屋基底经完好密封时,墙地砖的放射性就成了室内氡的主要来源。
5、煤气通常称液化气或天然气,往往有着相对高的氡浓度。
氡对人体的主要伤害是什么?
专家们把氡称为“导致人类肺癌的第二大‘杀手’”,是除吸烟以外引起肺癌的第二大因素。世界卫生组织把氡列为使人致癌的19种物质之一。
如何降低居室中的氡?
1、不要购买建筑在富铀区、伽玛高值区、断裂构造区的楼宇。要知道室内的氡含量是否超标,最有效的方法就是进行室内氡浓底的检测,个人购买住房时,也应考虑这个因素。
2、在装饰装修时,要尽量按照国家标准选用放射性含量低的建筑和装饰材料。
3、室内装饰中,要注意填平、密封地板和墙上的所有裂缝,特别是地下室、一层和平房的住户更要如此。
4、做好室内通风换气,这是最简便、最省钱的方法。门窗关闭的房屋内,氡的浓度往往比敞开门窗时高数倍到数十倍。专家曾做过试验,一间氡浓度在151贝可/m3 房间,开窗1小时后,室内氡浓度可降为48贝可/m3。如果配备优质的室内空气净化器更好。
5、孩子与妇女比成年男性更易受氡侵害,应尽量减少或禁止在室内吸烟。
国外相关报道:
美国环保署:http://www.epa.gov/radon/healthrisks.html
Lung cancer kills thousands of Americans every year. The untimely deaths of Peter Jennings and Dana Reeve have raised public awareness about lung cancer, especially among people who have never smoked. Smoking, radon, and secondhand smoke are the leading causes of lung cancer. Although lung cancer can be treated, the survival rate is one of the lowest for those with cancer. From the time of diagnosis, between 11 and 15 percent of those afflicted will live beyond five years, depending upon demographic factors. In many cases lung cancer can be prevented; this is especially true for radon.
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. Smoking causes an estimated 160,000* deaths in the U.S. every year (American Cancer Society, 2004). And the rate among women is rising. On January 11, 1964, Dr. Luther L. Terry, then U.S. Surgeon General, issued the first warning on the link between smoking and lung cancer. Lung cancer now surpasses breast cancer as the number one cause of death among women. A smoker who is also exposed to radon has a much higher risk of lung cancer.
Radon is the number one cause of lung cancer among non-smokers, according to EPA estimates. Overall, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer. Radon is responsible for about 21,000 lung cancer deaths every year. About 2,900 of these deaths occur among people who have never smoked. On January 13, 2005, Dr. Richard H. Carmona, the U.S. Surgeon General, issued a national health advisory on radon. Visit www.cheec.uiowa.edu/misc/radon.html7 for more on a study by Dr. William Field on radon-related lung cancer in women.
Secondhand smoke is the third leading cause of lung cancer and responsible for an estimated 3,000 lung cancer deaths every year. About 1,000 of these are people that never smoked, and about 2,000 are former smokers. Smoking affects non-smokers by exposing them to secondhand smoke. Exposure to secondhand smoke can have serious consequences for children’s health, including asthma attacks, affecting the respiratory tract (bronchitis, pneumonia), and may cause ear infections.
Learning more about lung cancer. The following sources provide a wide range of good information about lung cancer, prevention, and treatment.
Why is radon the public health risk that it is?
EPA estimates that about 20,000 lung cancer deaths each year in the U.S. are radon-related. Exposure to radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Radon is an odorless, tasteless and invisible gas produced by the decay of naturally occurring uranium in soil and water. Radon is a form of ionizing radiation and a proven carcinogen. Lung cancer is the only known effect on human health from exposure to radon in air. Thus far, there is no evidence that children are at greater risk of lung cancer than are adults.
Radon in air is ubiquitous. Radon is found in outdoor air and in the indoor air of buildings of all kinds. EPA recommends homes be fixed if the radon level is 4 pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter) or more. Because there is no known safe level of exposure to radon, EPA also recommends that Americans consider fixing their home for radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. The average radon concentration in the indoor air of America’s homes is about 1.3 pCi/L. It is upon this level that EPA based its estimate of 20,000 radon-related lung cancers a year upon. It is for this simple reason that EPA recommends that Americans consider fixing their homes when the radon level is between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. The average concentration of radon in outdoor air is .4 pCi/L or 1/10th of EPA’s 4 pCi/L action level.
For smokers the risk of lung cancer is significant due to the synergistic effects of radon and smoking. For this population about 62 people in a 1,000 will die of lung-cancer, compared to 7.3 people in a 1,000 for never smokers. Put another way, a person who never smoked (never smoker) who is exposed to 1.3 pCi/L has a 2 in 1,000 chance of lung cancer; while a smoker has a 20 in 1,000 chance of dying from lung cancer. Figure A compares the risks between smokers and never smokers; smokers are at a much higher risk than never smokers, e.g., at 8 pCi/L the risk to smokers is six times the risk to never smokers.
The radon health risk is underscored by the fact that in 1988 Congress added Title III on Indoor Radon Abatement to the Toxic Substances Control Act. It codified and funded EPA’s then fledgling radon program. Also that year, the Office of the U.S. Surgeon General issued a warning about radon urging Americans to test their homes and to reduce the radon level when necessary (U.S. Surgeon General).
Unfortunately, many Americans presume that because the action level is 4 pCi/L, a radon level of less than 4 pCi/L is ‘safe’. This perception is altogether too common in the residential real estate market. In managing any risk, we should be concerned with the greatest risk. For most Americans, their greatest exposure to radon is in their homes; especially in rooms that are below grade (e.g., basements), rooms that are in contact with the ground and those rooms immediately above them.
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime*... | The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**... | WHAT TO DO: Stop smoking and... |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/L | About 260 people could get lung cancer | 250 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 150 people could get lung cancer | 200 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 120 people could get lung cancer | 30 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L | About 62 people could get lung cancer | 5 times the risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L | About 32 people could get lung cancer | 6 times the risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L | About 20 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | (Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L | About 3 people could get lung cancer | (Average outdoor radon level) | |
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be lower. pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter) * Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). ** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention''s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Reports. | |||
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who never smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime*... | The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to**... | WHAT TO DO: |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 pCi/L | About 36 people could get lung cancer | 35 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 18 people could get lung cancer | 20 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 15 people could get lung cancer | 4 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L | About 7 people could get lung cancer | The risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L | About 4 person could get lung cancer | The risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L | About 2 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | (Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L | (Average outdoor radon level) | ||
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be higher. pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter) * Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). ** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention''s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Reports. | |||
产品名称: REN500A型智能化х、γ辐射仪
产品描述: REN500A型智能化х、γ辐射仪(又叫环境监测用X、γ辐射空气比释动能(吸收剂量)率仪或便携式X、γ辐射周围剂量当量率仪)采用高灵敏的闪烁晶体作为探测器,反应速度快,具有较宽的剂量率测量范围。 该仪器除能测高能、低能γ射线外,还能对低能X射线进行准
产品名称: REN500T长杆x-γ剂量率仪
产品描述: REN500T是手持式仪表可用来监测X、γ辐射剂量率。用于各种γ辐射场或环境γ辐射的监测工作。仪器配有伸缩长杆,可用于测量人员不易到达或有较强放射性存在的场所,为使用人员提供有效保护。此外通过配套的RenRiRate辐射剂量管理软件可将存
产品名称: REN710型行人通道式γ射线安检门
产品描述: REN710型行人通道式γ射线安检门是专为行人设计的、用于检测放射性物质的门式检测系统,它为行人非法携带放射性物质及特殊核材料提供快速检测手段,能够为海关、机场、码头、火车站、医院、边境检查、重要会议场所安全检查提供帮助。是核
产品名称: REN200B型X-γ个人剂量报警仪
产品描述: REN200B型X、γ辐射个人剂量当量HP(10)监测仪(简称:个人剂量报警仪)内置高量程盖格计数管为探测器,主要用来监测各种放射性工作场所的X、γ以及硬β射线的辐射,具有较宽的测量范围。能显示工作场所的剂量当量率和累积剂量,更换电池时,日期及累积数据能永久保存。可选配RenRiPersonal个人
产品名称: REN300A+REN-3He-N型固定式中子、伽玛报警仪
产品描述: 本报警仪由REN300A在线辐射安全报警仪和REN-3He-N中子探头和REN-GM-L X、伽玛探头组成。该辐射报警装置是采用特殊设计的前置放大电路,具有灵敏度高、操作方便、自动显示、数据存储和超阈值报警等特点,能实时给出x射线、γ射线、中子射线的辐射剂量率。考虑到现场操作、应急快速响应的需要,主
产品名称: 中子及X、γ、β外照射个人剂量监测服务
产品描述: 放射工作人员个人剂量委托监测服务 依据《GB18871-2002电离辐射防护与辐射源安全基本标准》和《GBZ128-2002职业性外照射个人监测规范》的要求,以热释光个人剂量计作为监测手段,为放射工作人员提供个人剂量委托监测服务,并为企业或卫生行政部
产品名称: REN800型中子周围剂量当量(率)仪
产品描述: REN800型中子周围剂量当量(率)仪 采用高灵敏的进口He-3管作为探测器,反应速度快。该仪器使用方便;灵敏度高、抗γ性能好、能量响应特性好,即可用作便携式仪器又可用作固定式中子剂量监测仪。此外通过配套的RenRiRate辐射剂量管理软件可将存储的
产品名称: REN600型α、β表面污染测量仪
产品描述: REN600Bα、β表面污染检测仪采用闪烁探测法,用来检测放射性工作场所和实验室的工作台面、地板、墙面、手、衣服、鞋等表面受α或β(γ)放射性污染的程度,也可对密封型α、β同位素泄漏水平进行检测。仪器具有较高的探测效率;此外通过配套的 RenRiRate辐射剂量管理软件可将存储的数据读

,个人剂量报警器,个人射线剂量仪,辐射个人计量报警仪,个人核辐射仪,个人辐射监测仪,个人辐射剂量报警仪
上海仁日辐射防护设备有限公司(Shanghai Renri Radiation Protection Equipment Co., Ltd.) 上海仁日科贸有限公司 版权所有
电话:021-69515711 手机:13818065015 传真:021-69515712 Email:market@renri.com.cn
QQ:1993509414 地址:上海市曹安路1509号福瑞大厦516室 邮编:201824